Holistic Pregnancy & Birth Support
Natural Birth
Compass Program
Eliminate the Fear of Unknowns and Prepare for a Peaceful, Natural Birth
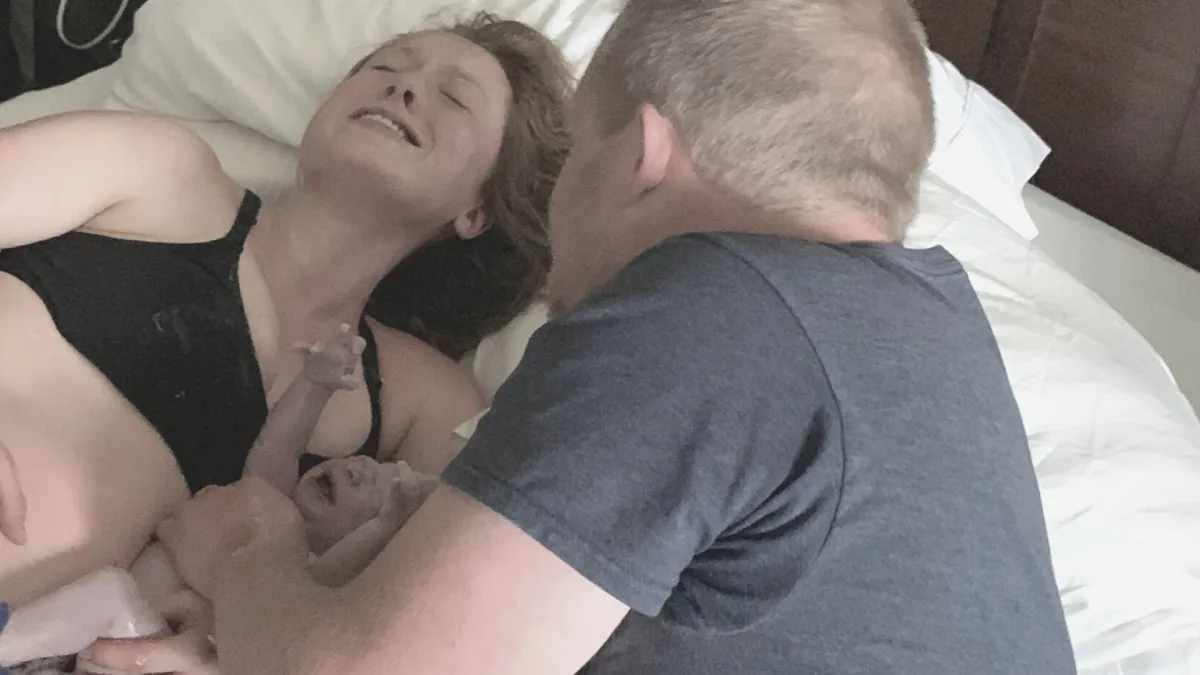
Natural Birth Compass Program Resources Support:
Family-led birth
Nature-led birth
Undisturbed birth
I have searched time and place to learn how to lead the birth culture back toward nature-led birth so families can confidently take birth back into their own hands and bring their baby into the world undisturbed and unharmed, just as nature intended.
You can birth safely & powerfully with nature as your guide!
Online Courses

Natural Birth Compass Physiologic Birth & Prenatal Wellness Program
The full, signature course with everything you need to know for making informed decisions about your prenatal care and birth so you are in control of your pregnancy & birth experience. Includes all the mini courses plus a complete physiologic birth course and prenatal wellness tools.

Beyond the Birth Plan: Craft Your Ideal Birth Approach in 2 hours!
Craft a birth plan that gives you confidence & peace of mind! This course includes the essential four components and 18 specific questions will guide you through everything you need to know for your perfect plan!

Circle Magic for Homebirth: A Mini Course Beyond the Ordinary
This mini-course explores birth from the Elements Earth, Air, Fire & Water, plus the four phases of who you are as a woman in the Great Cycle of Life, to help you prepare for the transformation from maiden to mother.

Physiologic Birth Mini-Course
Take a journey through physiologic birth that will merge the technical aspects of birth, like the stages of labor, cervical dilation, and monitoring contractions with the actual journey your baby takes through birth with stunning visual images that reinforce the beautiful design of natural birth.

Listen to the Podcast
The Unschooled Homebirth podcast is the place where we throw away the conventional birth textbooks and talk about homebirth from the philosophy of nature, life, and deep universal truths. Listen wherever you get podcasts or click the button below to stream online.
Hello!
I'm Tristin, and I love helping women optimize their prenatal health and have a fulfilling birth.
My focus is helping women reduce the risk of pregnancy and birth complications with holistic approaches so they can have the birth they want and avoid interventions they don't need.
After earning my Master's degree in Chinese medicine from Bastyr University in Seattle in 2006, I opened a private practice specialized in fertility and prenatal care.
Though my education was of the highest standards for Chinese medicine, and it prepared me technically for practice, I felt that something was missing from my knowledge base.
After studying with several amazing teachers who provided more technical knowledge, in 2011 I finally found the mentor who would provide me the insights into Chinese medicine I was looking for that helped me become a more holistic practitioner.
In the coming years, my mentor, Dr Yaron Seidman, and I would publish a book, Hunyuan Fertility: Conception, Babies & Miracles.
Along the way, I have also earned certificates in childbirth education, clinical whole foods nutrition, breathwork facilitation, the Body Ready Method© for pregnancy and birth, as well as the Holistic Doula training and a 10-month immersion in Quantum Midwifery practices from the Matrona with the wise one Whapio.
With the knowledge shared with me by my wise mentors, I have developed unique courses for natural pregnancy and birth to help women be able to say "I loved being pregnant and giving birth!".
Please reach out if you would like to learn more about the approach I have used to help hundreds of natural birthing families prepare for their births - it would be an honor to share any part of your pregnancy journey with you 💜.




